zurück
Oman unter
Wasser Muränen Clownfische Drückerfisch Falterfisch Feldermausfisch
Wasserschildkröte
Unterwasserbilder
Das Highlight die
Seeschildkröte
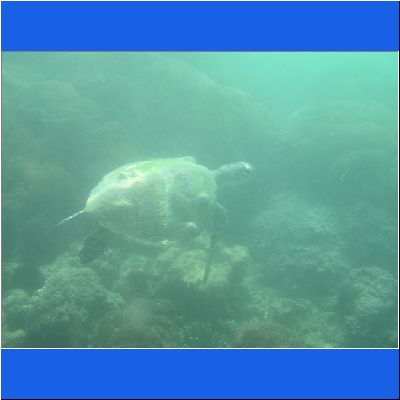
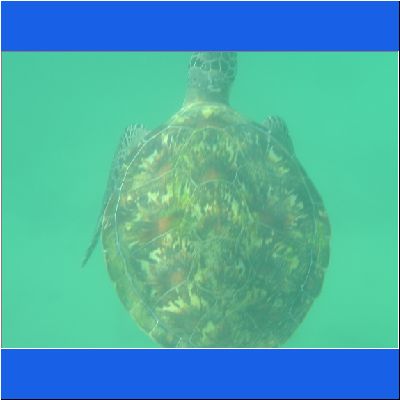
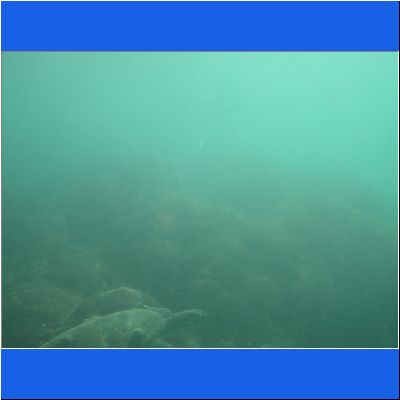
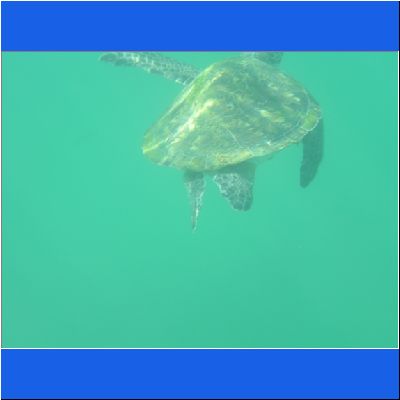
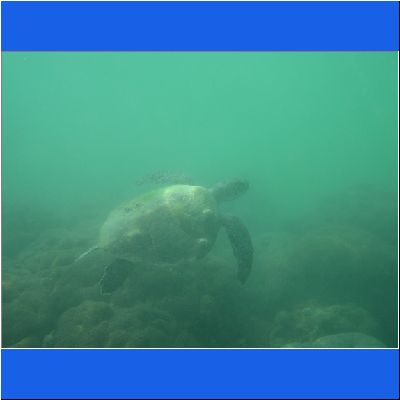
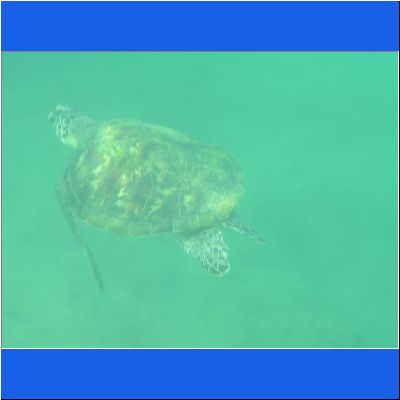
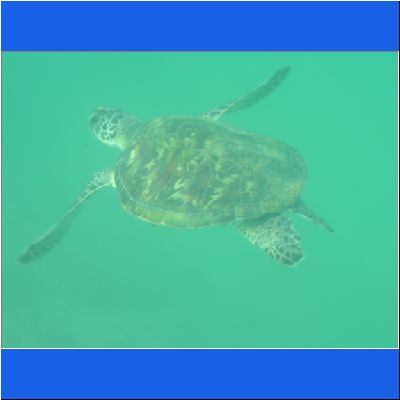
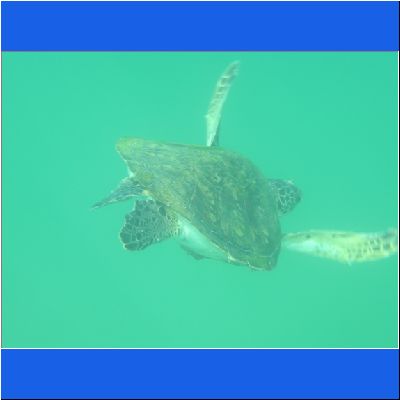
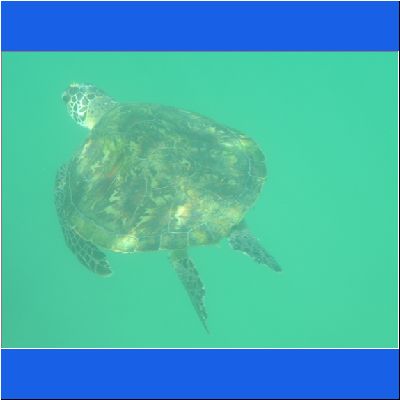
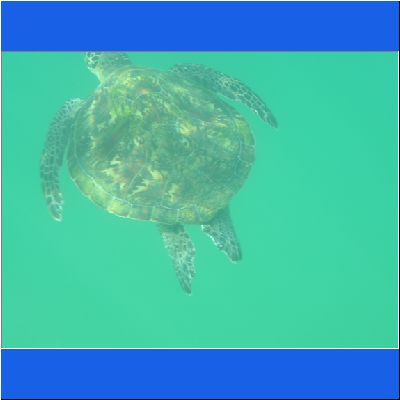
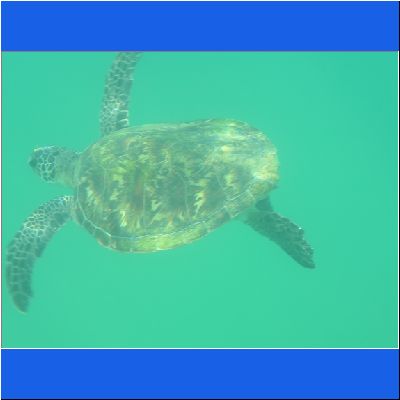
















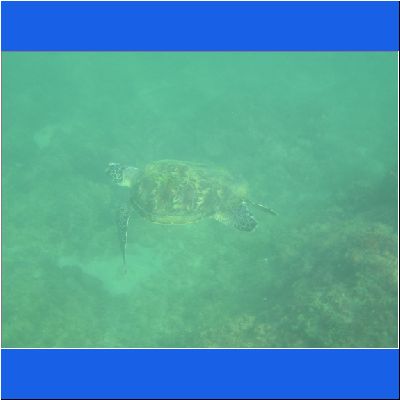

Schnorcheltour Arabisches Meer
Strasse von Hormouz




























Seaturtle Schnorcheln Oman Schildkroete Wasserschildkröte Oman
Sultanat Oman Maskat Mascat Oman Muskat Muscat Wahiba Sands Nizwa Rustaq Wadi
Tiwi Muttrah-Souk Jabreen Birkat Al Mauz Salalah Sumhurum Provinz Dhofar,
The Strait
of Hormuz (Arabic: مضيق هرمز,
Madiq Hormuz) is a narrow waterway that
connects the Persian Gulf to
the Gulf of Oman and, by
extension, the Arabian Sea. It
is one of the most strategic and critical maritime chokepoints in the world,
both for international trade and for regional geopolitical dynamics. The strait
plays a vital role in global energy transportation, particularly for the
oil and
natural gas industries.
Key Features of the
Strait of Hormuz:
1.
Geography and Location
-
Strategic Waterway: The Strait of Hormuz is about
33 kilometers (20 miles)
wide at its narrowest point, between the coasts of
Oman to the southeast and
Iran to the north. The
strait forms the boundary between the
Persian Gulf and the
Gulf of Oman.
-
Connecting Waters: The
strait connects the Persian Gulf,
home to significant oil reserves, to the
Arabian Sea and, via the
Gulf of Oman, to the
broader Indian Ocean. It
serves as a vital access route for shipping between the Gulf states and
international markets.
2.
Economic Significance
-
Global Oil Trade: The
Strait of Hormuz is one of the world's most important shipping lanes for
oil transport, as a
significant percentage of global oil exports pass through it. It is
estimated that nearly 20-30%
of the world’s seaborne oil trade
flows through this narrow waterway. Countries like
Saudi Arabia,
Iran,
Kuwait,
Iraq, and the
United Arab Emirates
(UAE) rely on this route for their oil exports.
-
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG):
In addition to oil, the strait is also crucial for the transport of
natural gas (especially
LNG) from the Gulf states
to international markets, making it a vital route for global energy supply.
3.
Strategic and Military Importance
-
Geopolitical Tensions:
Given the significance of the Strait of Hormuz to global energy trade, it
has become a key focus of geopolitical and military tensions, especially
between Iran and other
international powers. Iran has often emphasized its control over the strait
as a matter of national security and has made various threats to block or
close the strait in response to political or military confrontations.
-
Naval Presence: The
strait is heavily patrolled by naval forces from countries around the world,
including the United States,
which maintains a significant military presence in the Gulf region. Other
countries in the region, such as the UAE and Oman, also have security
interests in keeping the strait open for global trade.
4.
Shipping and Transportation
-
Shipping Traffic: The
Strait of Hormuz is one of the busiest maritime routes in the world. Every
day, many oil tankers, cargo ships, and other vessels pass through the
strait. The narrowness of the strait, combined with heavy shipping traffic,
makes navigation challenging, and there are occasional risks of collisions
or maritime accidents.
-
Key Ports: On the
southern side of the strait, the ports of
Dubai (UAE) and
Muscat (Oman) are vital
hubs for global trade. On the northern side, Iran's
Bandar Abbas and other
ports serve as important outlets for the country’s exports.
5.
Environmental Considerations
-
Marine Ecosystem: The
Persian Gulf is home to a variety of unique marine species, and the Strait
of Hormuz is an important area for marine biodiversity. The delicate
ecosystem faces environmental pressures from shipping, oil drilling, and
pollution. Efforts to protect marine life, including endangered species, are
ongoing in the region.
-
Pollution and Oil Spills:
Given the heavy traffic of oil tankers and cargo ships, the strait is prone
to the risk of oil spills
and other forms of maritime pollution, which can have long-lasting effects
on the surrounding environment.
6.
Security and Blockage Concerns
-
Blockade Threats: The
Strait of Hormuz has been a site of military posturing and tensions over the
years, particularly in times of regional conflict. In 2019, for example,
tensions between Iran and the United States led to concerns that Iran might
block the strait in retaliation for sanctions or military actions. Any
blockage of the strait would disrupt global oil supplies and severely impact
the global economy.
-
Freedom of Navigation:
International laws governing freedom of navigation in international waters
have been a point of contention. The strait is considered an
international waterway,
but Iran and some other
countries have emphasized territorial claims over the waters. This has
occasionally led to military
confrontations and diplomatic disputes.
7.
Oman’s Role and Neutrality
-
Oman’s Strategic Position:
Oman plays a key role in the security and stability of the Strait of Hormuz
due to its location on the southeastern side of the strait. Oman has long
been a neutral party in the region's political and military affairs, and it
has worked to maintain peaceful relations with all sides, including Iran and
the Gulf Arab states.
-
Diplomatic Efforts: Oman
has frequently acted as a mediator in disputes and has worked to avoid
military escalation in the region. Oman’s neutral stance has made it a key
player in maintaining stability in the Gulf.
8.
Tensions and Escalation
-
Recent Tensions: The
Strait of Hormuz has been a point of heightened tension in recent years,
particularly after incidents such as the
attack on oil tankers in
2019 and the downing of drones.
These tensions have sparked fears of conflict, especially between
Iran and the
United States, as well as
with other global powers that rely on the safe passage of ships through the
strait.
-
Global Impact: Any
closure or significant disruption to the Strait of Hormuz would have a
global economic impact, as it would disrupt the flow of oil and natural gas
to many countries, leading to potential
energy shortages,
price hikes, and
disruptions in international trade.
Conclusion:
The Strait of Hormuz is an
immensely important waterway for both global trade and regional security. Its
narrow passage and strategic location make it a key choke point in global oil
transportation. While it is a vital lifeline for energy exports from the
Persian Gulf, it is also a
region fraught with geopolitical tensions, particularly involving
Iran,
the United States, and other
countries in the region. The stability of the Strait of Hormuz is crucial not
only for the Middle East but also for the global economy, making it a
significant focal point in international relations and security concerns.
 04.10.25 Copyright Dirk
Rauschenbach Koelnerstrasse 293 51702 Bergneustadt
Datenschutzerklaerung 02261 9788972 Mail ccooly(
at) web.de
04.10.25 Copyright Dirk
Rauschenbach Koelnerstrasse 293 51702 Bergneustadt
Datenschutzerklaerung 02261 9788972 Mail ccooly(
at) web.de
 Safaris
Bergsteigen
Wandern
Inselwandern Weltweit
Safaris
Bergsteigen
Wandern
Inselwandern Weltweit
 Europa
Inselwandern
Europa
Inselwandern
 Städtewandern
Städtewandern
 Paintings
Paintings  Dirk Rauschenbach
Dirk Rauschenbach
 Safaris
Bergsteigen
Wandern
Inselwandern Weltweit
Safaris
Bergsteigen
Wandern
Inselwandern Weltweit
 Europa
Inselwandern
Europa
Inselwandern
 Städtewandern
Städtewandern
 Paintings
Paintings  Dirk Rauschenbach
Dirk Rauschenbach















![]() 04.10.25 Copyright Dirk
Rauschenbach Koelnerstrasse 293 51702 Bergneustadt
Datenschutzerklaerung 02261 9788972 Mail ccooly(
at) web.de
04.10.25 Copyright Dirk
Rauschenbach Koelnerstrasse 293 51702 Bergneustadt
Datenschutzerklaerung 02261 9788972 Mail ccooly(
at) web.de